Array
Now, we are able to declare required number of variables,
like suppose if we want 5 int type variable then we can declare it like –
int a,b,c,d,e ;
What if we want to declare 100 such variable …?? Then we
cannot use the above method as it is not convenient.
Hence, Array were introduced.
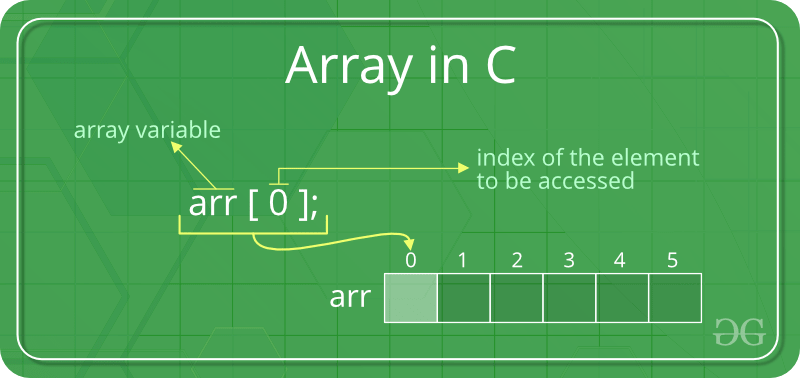
Array is a collection of variables of the same type that are referenced by a common name.
Syntax:
Base_type/data_type
array_name[size] ;
/* Like we want to declare 100 int type variable then we
use the method defined below */
int lol[100] ;
/* here , int is the base/data type and lol is the array
name given by the programmer .*/
We can also say that string is an array of character
datatype.
Array are of three types 1-Dimension Array , 2-Dimension
Array, 3-Dimension Array.
Array always starts from 0 and last element is size of
array minus 1.
i.e. a[20] has first element as a[0] and last element
as a[19] , so, total 20 elements.
Write a program to take input of 10 numbers from user
and count the positive numbers.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main(){
clrscr();
int number[10];
cout<<”\n We want you to enter 10 numbers ” ;
int counter=0;
for( int pos=0 ; pos<10 ; pos++)
{
cout<<”\n
Enter ”<<pos<<”th number = ”;
cin>>number[pos] ;
if
(number[pos]>=0)
{ counter = counter+1 ; }
}
cout<<”\n Total positive numbers are = ”<<counter;
cout<<”\n All the numbers given by you are = ”;
for ( pos=0 ; pos<10 ; pos++ )
{
cout<<”\t”<<number[pos]
;
}
getch();
}
Types of Array
1-Dimension Array, 2-Dimension Array, 3-Dimension
Array
1-Dimension Array is shown above.
2-Dimension Array and 3-Dimension Array are
an array in which each element is itself an array.
Write a program to store marks of 5 subjects of 2 students and also calculate their average marks.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main(){
int data[2][6];
for (int student=0 ; student<2 ; student++ )
{
cout<<"\n Data of Student " ;
for (int subject=0 ; subject<5 ; subject++ )
{
cout<<"\n Enter the Subject marks = ";
cin>>data[student][subject] ;
}
}
int sum ;
float avg;
for (int student=0 ; student<2 ; student++)
{
sum =0 ;
for (int subject=0 ; subject<6 ; subject++)
{
if (subject==5)
{
avg = sum/5;
data[student][subject] = avg ;
cout<<"average of
student"<<student<<” is = ”<<data[student][subject] ;
cout<<endl ;
}
else
{
sum = sum + data[student][subject] ;
}
}
}
getch();
}
Write a program for a salesman who wants to check his
average sale of 2 years by adding the sales of every month of a year.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main(){
clrscr();
int salesman_data[2][12] ;
float avg;
int sum ;
for (int year = 0 ; year<2 ; year++ ) {
sum =0 ;
cout<<”Data of Year " ;
for (int month=0 ; month<12 ; month++ ){
cout<<”\n
Enter the sale of Month " ;
cin>>salesman_data[year][month] ;
sum = sum +
salesman_data[year][month] ;
}
avg = sum /12 ;
cout<<”\n Average sale of this year ”<<avg ;
}
getch();
}


0 comments:
Post a Comment
Please give your valuable suggestions